One of many questions that has maybe been central to my very own analysis in blockchain expertise is: in the end, what’s it even helpful for? Why do we want blockchains for something, what sorts of companies ought to be run on blockchain-like architectures, and why particularly ought to companies be run on blockchains as a substitute of simply dwelling on plain outdated servers? Precisely how a lot worth do blockchains present: are they completely important, or are they simply good to have? And, maybe most significantly of all, what’s the “killer app” going to be?
Over the previous couple of months, I’ve spent a number of time excited about this situation, discussing it with cryptocurrency builders, enterprise capital companies, and notably folks from outdoors the blockchain house, whether or not civil liberties activists, folks within the finance and funds business or anyplace else. Within the means of this, I’ve come to quite a few necessary, and significant, conclusions.
First, there might be no “killer app” for blockchain expertise. The rationale for that is easy: the doctrine of low-hanging fruit. If there existed some specific software for which blockchain expertise is massively superior to anything for a good portion of the infrastructure of contemporary society, then folks can be loudly speaking about it already. This will likely seem to be the old economics joke about an economist discovering a twenty greenback invoice on the bottom and concluding it should be pretend as a result of in any other case it could have already got been taken, however on this case the state of affairs is subtly completely different: not like the greenback invoice, the place search prices are low and so choosing up the invoice is smart even when there may be solely a 0.01% likelihood it’s actual, right here search prices are very excessive, and loads of folks with billions of {dollars} of incentive have already been looking out. And to date, there was no single software that anybody has provide you with that has significantly stood out to dominate every little thing else on the horizon.
In reality, one can fairly fairly argue that the closest issues that we’ll ever need to “killer apps” are exactly these apps which have already been finished and recited and sensationalized advert nauseam: censorship resistance for Wikileaks and Silk Highway. Silk Highway, the net nameless drug market that was shut down by legislation enforcement in late 2013, processed over $1 billion in sales throughout its 2.5 years of operations, and whereas the payment-system-orchestrated blockade towards Wikileaks was in progress, Bitcoin and Litecoin donations have been responsible for the bulk of its revenue. In each circumstances the necessity was clear and the potential financial surplus was very excessive – earlier than Bitcoin, you’d don’t have any alternative however to purchase the medication in individual and donate to Wikileaks by cash-in-the-mail, and so Bitcoin supplied a large comfort acquire and thus the chance was snatched up virtually immediately. Now, nevertheless, that’s a lot much less the case, and marginal alternatives in blockchain expertise usually are not almost such simple grabs.
Whole and Common Utility
Does this imply, nevertheless, that blockchains have hit their peak utility? Most definitely not. They’ve hit peak necessity, within the sense of peak utility per consumer, however that isn’t the identical factor as peak utility. Though Silk Highway was indispensable for lots of the those that used it, even among the many drug-using group it is not indispensable usually; as a lot because it befuddles this specific writer how strange people are alleged to get such connections, most individuals have in some way discovered “a man” that they know that they’ll buy their weed from. Curiosity in smoking weed in any respect appears to strongly correllate with having easy accessibility to it. Therefore, within the grand scheme of issues, Silk Highway has solely had an opportunity to change into related to a really area of interest group of individuals. Wikileaks is comparable; the set of people that care about company and governmental transparency strongly sufficient to donate cash to a controversial group in help of it’s not very giant in comparison with the whole inhabitants of the world. So what’s left? Briefly, the lengthy tail.
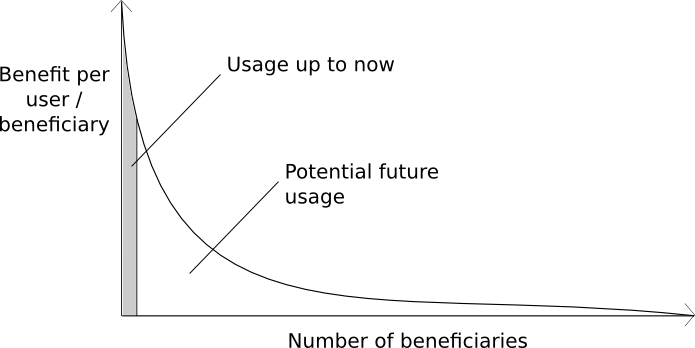
So what’s the lengthy tail? That is the place it will get arduous to elucidate. I might present an inventory of purposes which are included on this “lengthy tail” of purposes; nevertheless, blockchains usually are not indispensable, and don’t even supply extraordinarily robust basic benefits for every one. For every particular person case, an advocate of both the “blockchain purposes are overrated, it is the Bitcoin foreign money that issues” or the “blockchain tech as a complete is ineffective” place can fairly fairly provide you with a method to implement the scheme simply as simply on a centralized server, change blockchain governance with a authorized contract, and apply no matter different replacements to show the product into one thing way more just like a conventional system. And on that time, they’d be utterly appropriate: for that exact use case, blockchains usually are not indispensable. And that is the entire level: these purposes usually are not on the high of the distribution, up there with Wikileaks and Silk Highway; in the event that they have been, they’d have been carried out already. Within the lengthy tail, blockchains usually are not obligatory; they’re handy. They’re merely marginally higher than the following accessible instrument for the job. And but, as a result of these purposes are way more mainstream, and might profit a whole lot of hundreds of thousands of customers, the overall acquire to society (which might be seen from the world on the above chart) is way bigger.
Maybe one of the best analogy to this line of reasoning is to ask the next rhetorical query: what’s the killer app of “open supply”? Open supply has clearly been an excellent factor for society, and it’s getting used for hundreds of thousands of software program packages world wide, however however it’s nonetheless arduous to reply the query. And the reason being the identical: there isn’t a killer app, and the record of purposes has a really very lengthy tail – mainly, nearly each sort of software program conceivable, with specific emphasis on lower-level libraries that find yourself reused by hundreds of thousands of initiatives many occasions over and important cryptographic safety libraries.
Blockchains, Redefined… Once more
Now, what are the particular advantages of blockchains that make the lengthy tail worthwhile? To start out off, let me present the present description that I take advantage of of what a blockchain is:
A blockchain is a magic pc that anybody can add applications to and go away the applications to self-execute, the place the present and all earlier states of each program are at all times publicly seen, and which carries a really robust cryptoeconomically secured assure that applications working on the chain will proceed to execute in precisely the way in which that the blockchain protocol specifies.
Discover that this definition does NOT:
- Use financially-charged phrases like “ledger”, “cash” or “transactions”, or certainly any phrases geared towards a specific use case
- Point out any specific consensus algorithm, or certainly point out something in regards to the technical properties of how a blockchain works (apart from the truth that it is “cryptoeconomic”, a technical time period roughly which means “it is decentralized, it makes use of public key cryptography for authentication, and it makes use of financial incentives to make sure that it retains going and would not return in time or incur another glitch”)
- Make a restriction to any specific kind of state transition perform
The one factor that the definition does nicely is clarify what a blockchain does, and it explains it in such a method that any software program developer will be capable to pretty clearly have at the very least an intuitive grasp of its worth proposition. Now, in observe, typically the programming language that the applications run in could be very restrictive; Bitcoin’s language might be seen as requiring a sequence of DESTROY COIN:
The one factor that the definition emphasizes extraordinarily nicely is that blockchains usually are not about bringing to the world anyone specific ruleset, whether or not it is a foreign money with a fixed-supply financial coverage, a reputation registry with a 200-day re-registration time, a specific decentralized trade design or no matter else; fairly, they’re about creating the liberty to create a brand new mechanism with a brand new ruleset extraordinarily rapidly and pushing it out. They’re Lego Mindstorms for constructing financial and social establishments.
That is the core of the extra average model of the “it is the blockchain that is thrilling, not the foreign money” place that’s so prevalent in mainstream business: it’s certainly true that foreign money is important to make cryptoeconomic blockchains work (though NOT blockchain-like information buildings following the Stellar subjective consensus model), however the foreign money is there merely as financial plumbing to incentivize consensus participation, maintain deposits and pay transaction charges, not because the center-stage level of speculative mania, shopper curiosity and pleasure.
Now, why are blockchains helpful? To summarize:
- You may retailer information on them and that information is assured to have a really excessive diploma of availability
- You may run purposes on them and be assured an especially excessive uptime
- You may run purposes on them, and be assured an especially excessive uptime going very far into the long run
- You may run purposes on them, and persuade your customers that the appliance’s logic is trustworthy and is doing what you might be promoting that it does
- You may run purposes on them, and persuade your customers that your software will stay working even when you lose curiosity in sustaining it, you might be bribed or threatened to govern the appliance state in a roundabout way, otherwise you purchase a revenue motive to govern the appliance state in a roundabout way
- You may run purposes on them, and provides your self the backdoor key whether it is completely obligatory, BUT put “constitutional” limiations in your use of the important thing – for instance, requiring a software program replace to cross by means of a public one-month ready interval earlier than it may be launched, or on the very least instantly notifying customers of software updates
- You may run purposes on them, and provides a backdoor key to a specific governance algorithm (eg. voting, futarchy, some sophisticated multicameral parliament structure), and persuade your customers that the actual governance algorithm in query is definitely in charge of the appliance
- You may run purposes on them, and people purposes can speak to one another with 100% reliability – even when the underlying platform has solely 99.999% reliability
- A number of customers or corporations can run purposes on them, and people purposes can work together with one another at extraordinarily excessive pace with out requiring any community messages, whereas on the identical time guaranteeing that every firm has complete management over its personal software
- You may construct purposes that very simply and effectively reap the benefits of the info produced by different purposes (eg. combining funds and popularity methods is probably the most important acquire right here)
All of these issues are useful not directly to billions of individuals world wide, doubtlessly notably in areas of the world the place extremely developed financial, monetary and social infrastructure presently merely doesn’t work in any respect (although expertise will typically must be mixed with political reforms to resolve lots of the issues), and blockchains are good at offering these properties. They’re notably clearly useful in finance, as finance is probably probably the most concurrently computationally and trust-intensive business on this planet, however they’re additionally useful in lots of different spots in web infrastructure. There do exist different architectures that may additionally present these properties, however they’re barely to reasonably much less good than blockchains are. Gavin Wooden has began describing this ideally suited computing platform as “the world pc” – a pc the state of which is shared amongst everybody and which a really giant group of individuals, which anybody is free to hitch, are concerned in sustaining.
Base Layer Infrastructure
Like open supply, by far the most important alternative for beneficial properties out of blockchain expertise are out of what might be known as “base-layer infrastructure” companies. Base-layer infrastructure companies, as a basic class, are characterised by the next properties:
- Dependency – there exist many different companies that intimately depend upon the base-layer service for performance
- Excessive community results – there are substantial advantages from very giant teams of individuals (and even everybody) utilizing the identical service
- Excessive switching prices – it’s troublesome for a person to modify from one service to the opposite
Word that one concern that isn’t in there may be any notion of uncooked “necessity” or “significance”; there might be pretty unimportant base layers (eg. RSS feeds) and necessary non-base-layers (eg. meals). Base-layer companies have existed ever since even earlier than the daybreak of civilization; within the so-called “caveman days” the one most necessary base-layer service of all was language. In considerably more moderen occasions, the first examples grew to become roads, the authorized system and postal and transportation methods, within the twentieth century we added phone networks and monetary methods, and on the finish of the millennium emerged the web. Now, nevertheless, the brand new base-layer companies of the web are virtually fully informational: web cost methods, id, area title methods, certificates authorities, popularity methods, cloud computing, varied sorts of knowledge feeds, and maybe within the close to future prediction markets.
In ten years time, the extremely networked and interdependent nature of those companies could make it such that it’s more durable for people to modify from one system to a different than it’s for them to even change which authorities they’re dwelling underneath – and that signifies that ensuring that these companies are constructed accurately and that their governance course of doesn’t put a couple of non-public entities in positions of maximum energy is of utmost significance. Proper now, many of those methods are in-built a extremely centralized trend, and that is partially merely resulting from the truth that the unique design of the World Vast Internet failed to comprehend the significance of those companies and embody defaults – and so, even in the present day, most web sites ask you to “sign up with Google” or “sign up with Fb”, and certificates authorities run into problems like this:
“A solo Iranian hacker on Saturday claimed duty for stealing a number of SSL certificates belonging to among the Internet’s largest websites, together with Google, Microsoft, Skype and Yahoo.
Early response from safety specialists was combined, with some believing the hacker’s declare, whereas others have been doubtful.
Final week, conjecture had targeted on a state-sponsored assault, maybe funded or performed by the Iranian authorities, that hacked a certificates reseller affiliated with U.S.-based Comodo.
On March 23, Comodo acknowledged the assault, saying that eight days earlier, hackers had obtained 9 bogus certificates for the log-on websites of Microsoft’s Hotmail, Google’s Gmail, the Web telephone and chat service Skype and Yahoo Mail. A certificates for Mozilla’s Firefox add-on web site was additionally acquired.”
Why should not certificates authorities be decentralized at the very least to the purpose of an M-of-N system once more? (Word that the case for way more widespread use of M-of-N is logically separable from the case for blockchains, however blockchains occur to be a superb platform to run M-of-N on).
Identification
Allow us to take a specific use case, “id on the blockchain”, and run with it. Usually, what do you want in an effort to have an id? The best reply is one we already know: you want to have a private and non-private key. You publish the general public key, which turns into your ID, and also you digitally signal each message you ship together with your non-public key, permitting anybody to confirm that these messages have been produced by you (the place, from their perspective, “you” means “the entity that holds that exact public key”). Nonetheless, there are a couple of challenges:
- What occurs in case your key will get stolen, and you want to change to a brand new one?
- What occurs should you lose your key?
- What if you wish to discuss with different customers by their names, and never only a random 20-byte string of cryptographic information?
- What if you wish to use a extra superior method for safety reminiscent of multisig, and never only a single key?
Allow us to strive fixing these challenges one-by-one. We are able to begin off with the fourth. A easy answer is that this: as a substitute of requiring one specific cryptographic signature kind, your public key turns into a program, and a legitimate signature turns into a string that, when fed into this system along with the message, returns 1. Theoretically, any single-key, multi-key or no matter different sort of ruleset might be encoded into such a paradigm.
Nonetheless, this has an issue: the general public keys will get too lengthy. We are able to resolve this by placing the precise “public key” into some information retailer (eg. a distributed hash table if we would like decentralization) and utilizing the hash of the “public key” because the consumer’s ID. This doesn’t but require blockchains – though, within the newest designs, within the restrict scalable blockchains are actually not that completely different in design from DHTs and so it’s fully potential that, in ten years time, each sort of decentralized system used for something will unintentionally or deliberately converge into some sort of scalable blockchain.
Now, think about the primary drawback. We are able to consider this because the certificate revocation drawback: if you wish to “revoke” a specific key, how do you make sure that it will get round to everybody who must see it? This by itself can as soon as once more be solved by a distributed hash desk. Nonetheless, this results in the following drawback: if you wish to revoke a key, what do you change it with? In case your secret is stolen, you and the attacker each have it, and so neither of you might be convincingly extra authoritative. One answer is to have three keys, after which if one will get revoked then require a signature from two or all of them to approve the following key. However this results in a “nothing at stake” drawback: if the attacker ultimately manages to steal all three of your keys from some level in historical past, then they’ll simulate a historical past of assigning a brand new key, assigning additional new keys from there, and your individual historical past is now not extra authoritative. This is a timestamping drawback, and so right here blockchains can truly assist.
For the second drawback, holding a number of keys and reassigning additionally works fairly nicely – and right here, blockchains usually are not wanted. In reality, you do not want to re-assign; with intelligent use of secret sharing you may truly get well from key losses just by preserving your key in “shards”, such that should you lose any single shard you may at all times use secret sharing math to easily get well it from the others. For the third drawback, blockchain-based title registries are the only answer.
Nonetheless, in observe most individuals usually are not well-equipped to securely retailer a number of keys, and there are at all times going to be mishaps, and sometimes centralized companies play an necessary function: serving to folks get their accounts again within the occasion of a mistake. On this case, the blockchain-based answer is easy: social M-of-N backup.
You decide eight entities; they might be your folks, your employer, some company, nonprofit and even sooner or later a authorities, and if something goes incorrect a mixture of 5 of them can get well your key. This idea of social multi-signature backup is probably one of the highly effective mechanisms to make use of in any sort of decentralized system design, and offers a really excessive quantity of safety very cheaply and with out counting on centralized belief. Word that blockchain-based id, notably with Ethereum’s contract mannequin, makes all of this very simple to program: within the title registry, register your title and level it at a contract, and have that contract keep the present important key and backup keys related to the id in addition to the logic for updating them over time. An id system, secure and easy-to-use sufficient for grandma, finished with none particular person entity (apart from you!) in management.
Identification isn’t the one drawback that blockchains can alleviate. One other part, intimately tied up with id, is popularity. At present, what passes for “popularity methods” within the fashionable world are invariably both insecure, resulting from their lack of ability to make sure that an entity score one other entity actually interacted with them, or centralized, tying popularity information to a specific platform and having the popularity information exist underneath that platform’s management. Once you change from Uber to Lyft, your Uber score doesn’t carry over.
A decentralized popularity system would ideally encompass two separate layers: information and analysis. Knowledge would consist of people making unbiased rankings about others, rankings tied to transactions (eg. with blockchain-based funds one can create an open system such you could solely give retailers a score should you truly pay them), and a set of different sources, and anybody can run their very own algorithm to guage their information; “light-client pleasant” algorithms that may consider a proof of popularity from a specific dataset rapidly could change into an necessary analysis space (many naive popularity algorithms contain matrix math, which has almost cubic computational complexity within the underlying information and so is tough to decentralize). “Zero-knowledge” popularity methods that enable a consumer to offer some sort of cryptographic certificates proving that they’ve at the very least x popularity factors based on a specific metric with out revealing anything are additionally promising.
The case of popularity is attention-grabbing as a result of it combines collectively a number of advantages of the blockchain as a platform:
- Its use as an information retailer for id
- Its use as an information retailer for reputational data
- Inter-application interoperability (rankings tied to proof of cost, means for any algorithm to work over the identical underlying set of knowledge, and so on)
- A assure that the underlying information might be transportable going into the long run (corporations could voluntarily present a popularity certificates in an exportable format, however they don’t have any method to pre-commit to persevering with to have that performance going into the long run)
- The usage of a decentralized platform extra usually to ensure that the popularity wasn’t manipulated on the level of calculation
Now, for all of those advantages, there are substitutes: we are able to belief Visa and Mastercard to offer cryptographically signed receipts {that a} specific transaction passed off, we are able to retailer reputational data on archive.org, we are able to have servers speak to one another, we are able to have non-public corporations specify of their phrases of service that they comply with be good, and so forth. All of those choices are fairly efficient, however they’re not almost as good as merely placing every little thing out into the open, working it on “the world pc” and letting cryptographic verification and proofs do the work. And an analogous argument might be made for each different use case.
Slicing Prices
If the most important worth from blockchain expertise comes on the lengthy tail, as this thesis suggests, then that results in an necessary conclusion: the per-transaction acquire from utilizing a blockchain could be very small. Therefore, the issue of chopping prices of consensus and growing blockchain scalability turns into paramount. With centralized options, customers and companies are used to paying basically $0 per “transaction”; though people trying to donate to Wikileaks could also be prepared to pay even a charge of $5 to get their transaction by means of, somebody attempting to add a popularity document could nicely solely be prepared to pay a charge of $0.0005.
Therefore, the issue of creating consensus cheaper, each within the absolute sense (ie. proof of stake) and within the per-transaction sense (ie. through scalable blockchain algorithms the place at most a few hundred nodes course of each transaction), is completely paramount. Moreover, blockchain builders ought to remember the fact that the final forty years of software program improvement has been a historical past of transferring to progressively much less and fewer environment friendly programming languages and paradigms solely as a result of they permit builders to be much less skilled and lazier, and equally work to design blockchain algorithms that work across the precept that builders are actually not going to be all that sensible and considered about what they placed on the blockchain and what they maintain off – although a well-designed system of transaction charges will seemingly result in builders naturally studying a lot of the necessary factors by means of private expertise.
Therefore, there may be substantial hope for a future that may be, to a considerable diploma, extra decentralized; nevertheless, the times of simple beneficial properties are over. Now could be the time for a a lot more durable, and longer, slog of wanting into the true world, and seeing how the applied sciences that we’ve got constructed can truly profit the world. Throughout this stage, we’ll seemingly uncover that in some unspecified time in the future we’ll hit an inflection level, the place most cases of “blockchain for X” might be made not by blockchain fans in search of one thing helpful to do, coming upon X, and attempting to do it, however fairly by X fans who have a look at blockchains and understand that they’re a reasonably useful gizmo for performing some a part of X. Whether or not X is web of issues, monetary infrastructure for the growing world, bottom-up social, cultural and financial establishments, higher information aggregation and safety for healthcare, or just controversial charities and uncensorable marketplaces. Within the latter two circumstances, the inflection level has seemingly already hit; lots of the unique crowd of blockchain fans grew to become blockchain fans due to the politics. As soon as it hits within the different circumstances, nevertheless, then we’ll actually know that it has gone mainstream, and that the most important humanitarian beneficial properties are quickly to come back.
Moreover, we’ll seemingly uncover that the idea of “the blockchain group” will stop to be significant as any sort of quasi-political motion in its personal proper; if any label applies in any respect, “crypto 2.0” is more likely to be probably the most defensible one. The reason being just like why we don’t have an idea of “the distributed hash desk group”, and “the database group”, whereas existent, is admittedly merely a set of pc scientists who occur to focus on databases: blockchains are only one expertise, and so in the end the best progress can solely be achieved by engaged on mixture with a complete set of different set of decentralized (and decentralization-friendly) applied sciences: reputation systems, distributed hash tables, “peer-to-peer hypermedia platforms“, distributed messaging protocols, prediction markets, zero-knowledge proofs and sure many extra that haven’t but been found.












